Conversion of molecular lines lists¶
Introduction¶
This section describes specific implementation details for conversion of molecular lines lists according to [Barbuy2018].
Source formats:
Robert Kurucz molecular line lists [Kurucz]
TurboSpectrum [Plez]
HITRAN/HITEMP 160-character format [Gordon2016]
VALD3 [VALD3] (to do)
Conversion output:
PFANT molecular lines file (such as “molecules.dat”)
How the conversion is made¶
Quoting [Barbuy2018]:
Line lists of molecular bands come however in different formats, and as well the different codes use these lists adapted in different ways. The main difference in using molecular line lists is the use of either the Einstein A coefficients, […] which are a sum of all ingredients, or when this is not available, the different constituents that produce the line.
List of symbols¶
Input molecular constants obtained from NIST database (all given in unit: cm**-1)¶
omega_e: vibrational constant – first term
omega_ex_e: vibrational constant – second term
omega_ey_e: vibrational constant – third term
B_e: rotational constant in equilibrium position
alpha_e: rotational constant – first term
D_e: centrifugal distortion constant
beta_e: rotational constant – first term, centrifugal force
A: Coupling counstant
M2l: multiplicity of the initial state (1 for singlet, 2 for doublet, 3 for triplet and so on)
M2l: multiplicity of the final state
LambdaL: Sigma/Pi/Delta/Phi of the initial state (0 for Sigma, 1 for Pi, 2 for Delta, 3 for Phi)
Lambda2L: Sigma/Pi/Delta/Phi of the initial state
Input data from line list files¶
lambda: wavelength (angstrom)
vl: vibrational quantum number of the initial state
v2l: vibrational quantum number of the final state
spinl
spin2l
JL: rotational quantum number of the initial state
J2l: rotational quantum number of the final state
Calculated outputs¶
The following values are calculated using application convmol.py and stored as a PFANT molecular lines file (such as “molecules.dat”).
Jl/J2l-independent¶
qv: Franck-Condon factor (FCF) [TRAPRB1970]
Bv: rotational constant
Dv: rotational constant
Gv: rotational constant
These terms are calculated as follows:
qv = qv(molecule, system, vl, v2l) is calculted using the TRAPRB code [TRAPRB1970]
The FCFs were already calculate for several
different molecules and are tabulated inside file "moldb.sqlite"
Bv = B_e - alpha_e * (v2l + 0.5)
Dv = (D_e + beta_e * (v2l + 0.5)) * 1.0e+06
Gv = omega_e * (v2l + 0.5) - omega_ex_e * (v2l + 0.5) ** 2 + omega_ey_e * (v2l + 0.5) ** 3 -
omega_e / 2.0 - omega_ex_e / 4.0 + omega_ey_e / 8.0
To calculate FCFs, we used the TRAPRB code [TRAPRB1970]. After compiled and in
the system path, the traprb command can be invoked from inside moldbed.py to calculate new FCFs, when needed.
Jl/J2l-dependent (i.e., for each spectral line)¶
LS: line strength for given by formulas in [Kovacs1969], Chapter 3; Hönl-London factor
S: normalized line strength
LS is calculated using a different formula depending on:
the multiplicities of the transition (currently implemented only cases where the initial and final state have same multiplicity)
the value and/or sign of (DeltaLambda = LambdaL - Lambda2l);
whether A is a positive or negative number;
the branch of the spectral line (see below how to determine the branch)
So:
formula = KovacsFormula(i, ii, iii, iv)
LS = formula(almost every input variable)
Todo
Explain term formulas “u+/-”, “c+/-”
Normalization of the line strength¶
Normalization is applied so that, for a given J2l,:
sum([S[branch] for branch in all_branches]) == 1
To achieve this:
S = LS * 2. / ((2 * spin2l + 1) * (2 * J2l + 1) * (2 - delta_k))
Where:
spin2l = (M2l-1)/2
How to determine the branch¶
The branch “label” follows one of the following conventions:
singlets: branch consists of a "<letter>", where letter may be either "P", "Q", or "R"
doublets, triplets etc:
if spin == spinl == spin2l: branch consists of "<letter><spin>"
if spinl <> spin2l: branch consists of "<letter><spinl><spin2l>"
The branch letter is determined as follows:
if Jl < J2l: "P"
if Jl == J2l: "Q"
if Jl > J2l: "R"
Where the conversion library is located¶
The line strength formulas from [Kovacs1969] are in module
pyfant.kovacs(source code directly available for inspection at https://github.com/trevisanj/pyfant/blob/master/pyfant/kovacs.py)The conversion routines are in subpackage
pyfant.convmol(source code at https://github.com/trevisanj/pyfant/tree/master/pyfant/convmol)
The convmol.py GUI for conversion of linelists¶
This section is a short tutorial on converting molecular linelists using the convmol.py GUI.
Note
Tool convmol.py only works safely for Kurucz format conversion. For other linelist format, in 2023 we
decided in favour of script building instead of maintaing the convmol.py GUI. See end of this section for more details.
Create a “project” directory
Run
moldbed.py(Figure 14) and press “Ctrl+D” to spawn a new molecular constants database in your local directory. The name of such file defaults to “moldb.sqlite”. This operation only needs to be carried out once in your local directoryDownload linelist file, e.g., from [Kurucz]
Run
convmol.pyIn the first tab (Figure 15)
Press “Ctrl+D” (only if the form is disabled)
Fill in the form as desired
Press “Ctrl+S” to save configuration file for this tab
In the second tab (
convmol1):press “Ctrl+D” (only if the form is disabled)
select “Kurucz” as data source on the left
locate linelist file
select isotope
most probably, check flags as in (
convmol1)specify output filename, or click on the plant button to make it up
Press “Ctrl+S” to save configuration file for this tab
Click on “Run conversion” button. Wait for conversion to complete
In the third tab (
convmol2), see details about the conversion session.
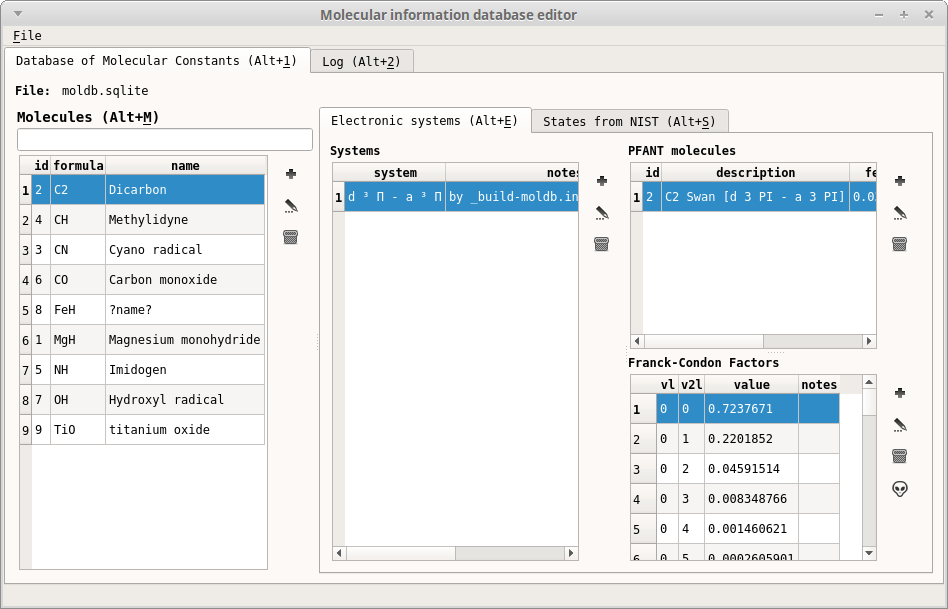
Figure 14 – First tab of convmol.py¶
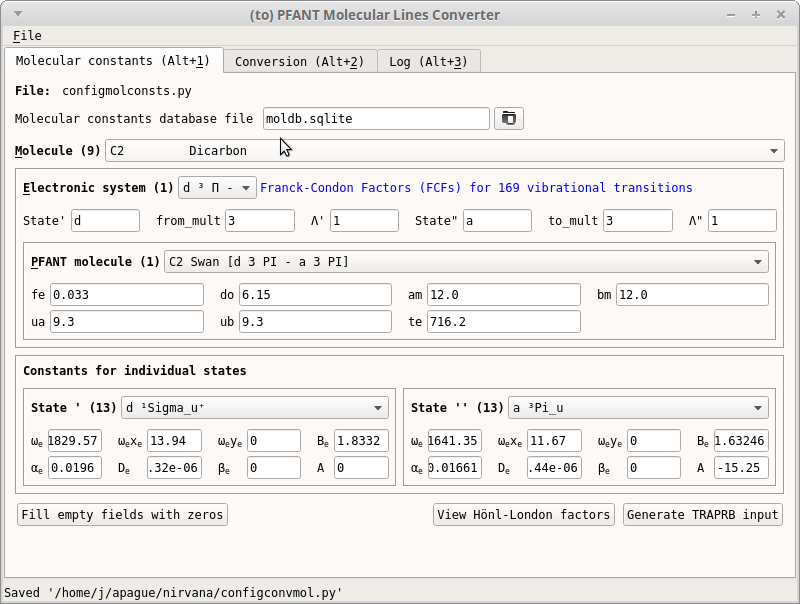
Figure 15 – First tab of convmol.py¶
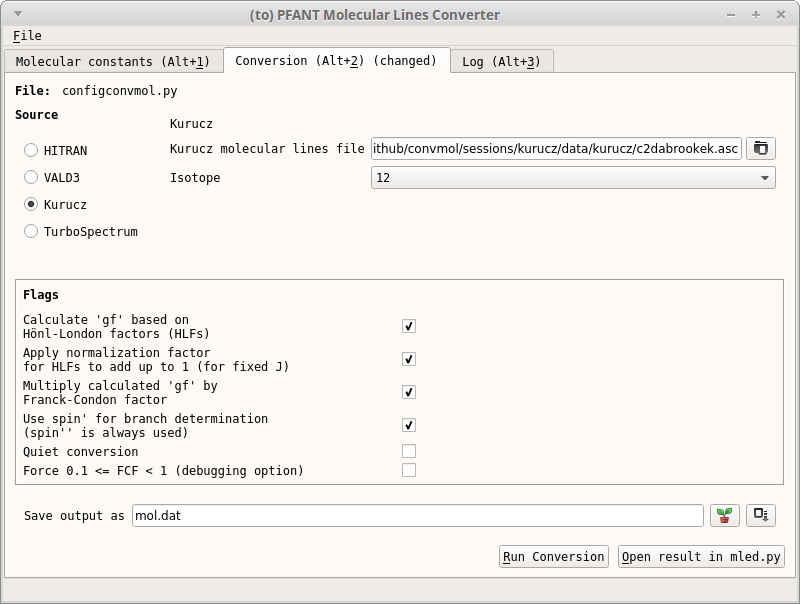
Figure 16 – Second tab of convmol.py¶

Figure 17 – Third tab of convmol.py¶
Conversion of HITRAN 160-character format¶
The following generates a PFANT molecular linelist from a HITRAN-like “.par” linelist.
A version of this code can also be found in the examples/convmol directory of the pyfant project
A molecular constants database (moldb.sqlite), and the following code creates one if not present. Such database
can be later edited using moldbed.py to adjust molecular constants (omega_e, omega_ex_e, omega_ey_e etc.)
if necessary.
In order to read the HITRAN-format linelist, we use the hapi library provided by HITRAN.
HITRAN-format conversion uses the Einstein coefficient A instead of the [Kovacs1969] line strength calculation. For
more details, see file conv_hitran.py in pyfant project.
# Example script of how to convert HITRAN molecular linelist to PFANT format
from f311 import hapi
import pyfant, a99, os
#=== BEGIN SETUP ===
DATADIR = "." # where hapi will look for ".par" files
DATANAME = "CO_dV11_stable-sample" # filename minus ".par" extension
ISOWANT = 1 # see ConvHitran class
FE = None # Line strength scaling factor for the whole molecule
SYSTEMID = "CO [X 1 Sigma - X 1 Sigma]" # Use moldbed.py to find out
#=== END SETUP
#=== BEGIN CONVERSION ===
fmoldb = pyfant.FileMolDB()
try:
fmoldb.load(os.path.join(DATADIR, fmoldb.default_filename))
except FileNotFoundError:
fmoldb.init_default()
molconsts = fmoldb.get_molconsts(SYSTEMID)
molconsts.None_to_zero()
hapi.VARIABLES['BACKEND_DATABASE_NAME'] = DATADIR
hapi.loadCache()
hapidata = hapi.LOCAL_TABLE_CACHE[DATANAME]
converter = pyfant.ConvHITRAN(comment=f"from {DATANAME}, iso={ISOWANT}",
molconsts=molconsts,
flag_quiet=True,
isowant=ISOWANT,
fe=FE)
fmol, log = converter.make_file_molecules(hapidata)
for line in str(log).split("\n"):
a99.get_python_logger().info(line)
fmol.save_as(f"{DATANAME}.PFANT.dat")
#=== END CONVERSION ===
Bibliography¶
Barbuy, B., Julio Trevisan, and A. de Almeida. “Calculation of molecular line intensity in stellar atmospheres.” Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia 35 (2018): e046.
Istvan Kovacs, Rotational Structure in the spectra of diatomic molecules. American Elsevier, 1969
Jarmain, W. R., and J. C. McCallum. “TRAPRB: a computer program for molecular transitions.” University of Western Ontario (1970)
I.E. Gordon, L.S. Rothman, C. Hill, R.V. Kochanov, Y. Tan, P.F. Bernath, M. Birk, V. Boudon, A. Campargue, K.V. Chance, B.J. Drouin, J.-M. Flaud, R.R. Gamache, J.T. Hodges, D. Jacquemart, V.I. Perevalov, A. Perrin, K.P. Shine, M.-A.H. Smith, J. Tennyson, G.C. Toon, H. Tran, V.G. Tyuterev, A. Barbe, A.G. Császár, V.M. Devi, T. Furtenbacher, J.J. Harrison, J.-M. Hartmann, A. Jolly, T.J. Johnson, T. Karman, I. Kleiner, A.A. Kyuberis, J. Loos, O.M. Lyulin, S.T. Massie, S.N. Mikhailenko, N. Moazzen-Ahmadi, H.S.P. Müller, O.V. Naumenko, A.V. Nikitin, O.L. Polyansky, M. Rey, M. Rotger, S.W. Sharpe, K. Sung, E. Starikova, S.A. Tashkun, J. Vander Auwera, G. Wagner, J. Wilzewski, P. Wcisło, S. Yu, E.J. Zak, The HITRAN2016 Molecular Spectroscopic Database, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. (2017). doi:10.1016/j.jqsrt.2017.06.038.
Horas - Descrição 10,5 - Análise preliminar 4,5 - Implementação da leitura separada de linelists moleculares no PFANT 6,0 - Conversão de linelist .bsyn –> PFANT 10,5 - Conversão de linelist HITRAN –> PFANT 4,0 - Comparações entre linelists convertidos e anterior (Melendez 1998) 19,0 - Testes e relatórios 4,0 - Correção de problemas em códigos relacionados ao Turbospectrum (B. Plez) 4,0 - Atualização de documentacao (https://trevisanj.github.io/PFANT)
ISSN Título Área de Avaliação Classificação 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO ADMINISTRAÇÃO PÚBLICA E DE EMPRESAS, CIÊNCIAS CONTÁBEIS E TURISMO B4 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO ARTES B4 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO BIODIVERSIDADE C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO BIOTECNOLOGIA C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO CIÊNCIAS AMBIENTAIS B2 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO CIÊNCIAS BIOLÓGICAS I C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO CIÊNCIAS BIOLÓGICAS II C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO CIÊNCIAS DA RELIGIÃO E TEOLOGIA C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO DIREITO B4 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO EDUCAÇÃO B4 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO EDUCAÇÃO FÍSICA B5 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO ENGENHARIAS I C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO ENGENHARIAS II B5 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO ENGENHARIAS III B5 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO ENSINO B1 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO FARMÁCIA C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO GEOCIÊNCIAS B5 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO GEOGRAFIA B4 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO HISTÓRIA C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO INTERDISCIPLINAR B3 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO MEDICINA II B5 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO NUTRIÇÃO C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO PLANEJAMENTO URBANO E REGIONAL / DEMOGRAFIA B4 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO PSICOLOGIA B4 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO QUÍMICA C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO SOCIOLOGIA C 1678-0701 EDUCAÇÃO AMBIENTAL EM AÇÃO ZOOTECNIA / RECURSOS PESQUEIROS C