Coding using the API¶
This section contains a series of examples on how to use the PFANT Fortran executables from a Python script. These “bindings” to the Fortran binaries, together with the ability to load, manipulate and save PFANT data files allow for complex batch operations.
Spectral synthesis¶
The following code generates Figure 1.
"""Runs synthesis over short wavelength range, then plots normalized and convolved spectrum"""
import pyfant
import f311
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Copies files main.dat and abonds.dat to local directory (for given star)
pyfant.copy_star(starname="sun-grevesse-1996")
# Creates symbolic links to all non-star-specific files, such as atomic & molecular lines,
# partition functions, etc.
pyfant.link_to_data()
# # First run
# Creates object that will run the four Fortran executables (innewmarcs, hydro2, pfant, nulbad)
obj = pyfant.Combo()
# synthesis interval start (angstrom)
obj.conf.opt.llzero = 6530
# synthesis interval end (angstrom)
obj.conf.opt.llfin = 6535
# Runs Fortrans and hangs until done
obj.run()
# Loads result files into memory. obj.result is a dictionary containing elements ...
obj.load_result()
print("obj.result = {}".format(obj.result))
res = obj.result
plt.figure()
f311.draw_spectra_overlapped([res["norm"], res["convolved"]])
plt.savefig("norm-convolved.png")
plt.show()
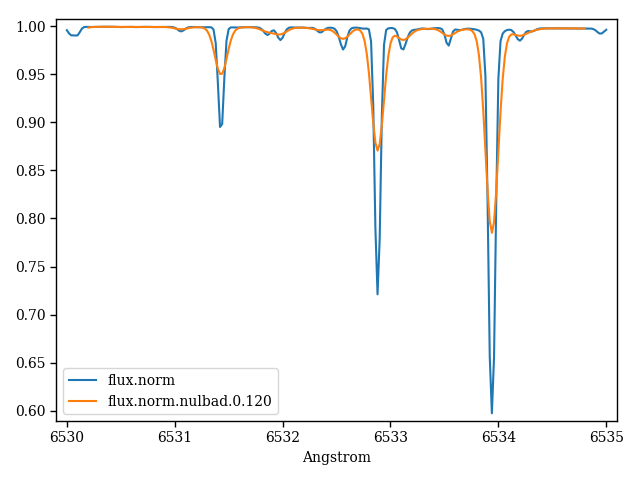
Figure 1 – pfant (file “flux.norm”) and nulbad outputs.¶
Spectral synthesis - convolutions¶
The following example convolves the synthetic spectrum (file “flux.norm”) with Gaussian profiles of different FWHMs (Figure 2).
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""Runs synthesis over short wavelength range, then plots normalized and convolved spectrum"""
import pyfant
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import a99
import f311
# FWHM (full width at half of maximum) of Gaussian profiles in angstrom
FWHMS = [0.03, 0.06, 0.09, 0.12, 0.15, 0.20, 0.25, 0.3, 0.5]
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Copies files main.dat and abonds.dat to local directory (for given star)
pyfant.copy_star(starname="sun-grevesse-1996")
# Creates symbolic links to all non-star-specific files
pyfant.link_to_data()
# # 1) Spectral synthesis
# Creates object that will run the four Fortran executables (innewmarcs, hydro2, pfant, nulbad)
ecombo = pyfant.Combo()
# synthesis interval start (angstrom)
ecombo.conf.opt.llzero = 6530
# synthesis interval end (angstrom)
ecombo.conf.opt.llfin = 6535
# Runs Fortrans and hangs until done
ecombo.run()
ecombo.load_result()
# Retains un-convolved spectrum for comparison
spectra = [ecombo.result["norm"]]
# # 2) Convolutions
for fwhm in FWHMS:
enulbad = pyfant.Nulbad()
enulbad.conf.opt.fwhm = fwhm
enulbad.run()
enulbad.load_result()
# Appends convolved spectrum for comparison
spectra.append(enulbad.result["convolved"])
# # 3) Plots
plt.figure()
f311.draw_spectra_overlapped(spectra)
K = 1.1
a99.set_figure_size(plt.gcf(), 1000*K, 500*K)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("many-convs.png")
plt.show()
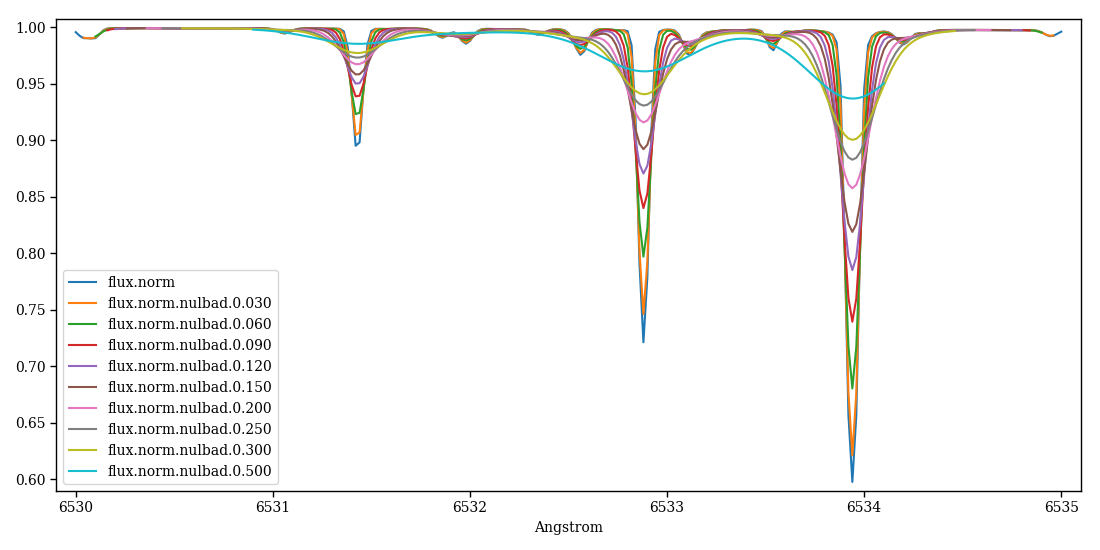
Figure 2 – single pfant output and several nulbad outputs.¶
Spectral synthesis - Continuum¶
The following code generates Figure 3.
"""Runs synthesis over large wavelength range, then plots continuum"""
import pyfant
import f311
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import a99
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Copies files main.dat and abonds.dat to local directory (for given star)
pyfant.copy_star(starname="sun-grevesse-1996")
# Creates symbolic links to all non-star-specific files, such as atomic & molecular lines,
# partition functions, etc.
pyfant.link_to_data()
# Creates object that will run the four Fortran executables (innewmarcs, hydro2, pfant, nulbad)
obj = pyfant.Combo()
oo = obj.conf.opt
# synthesis interval start (angstrom)
oo.llzero = 2500
# synthesis interval end (angstrom)
oo.llfin = 30000
# savelength step (angstrom)
oo.pas = 1.
# Turns off hydrogen lines
oo.no_h = True
# Turns off atomic lines
oo.no_atoms = True
# Turns off molecular lines
oo.no_molecules = True
obj.run()
obj.load_result()
print("obj.result = {}".format(obj.result))
res = obj.result
f311.draw_spectra_stacked([res["cont"]], setup=f311.PlotSpectrumSetup(fmt_ylabel=None))
K = .75
a99.set_figure_size(plt.gcf(), 1300*K, 450*K)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("continuum.png")
plt.show()
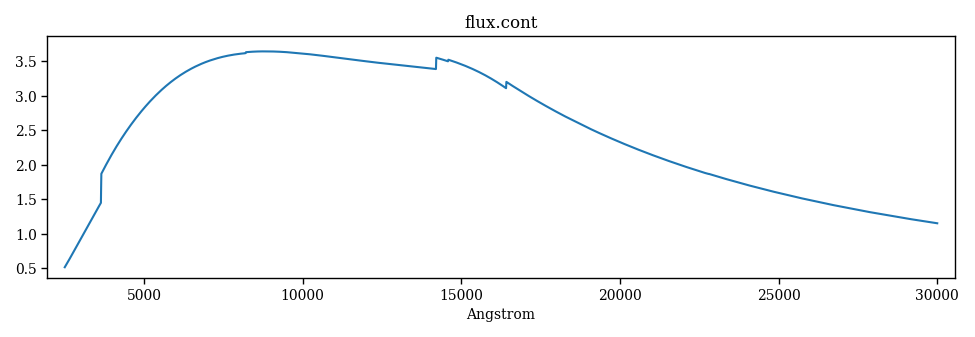
Figure 3 – continuum.¶
Spectral synthesis - Separate atomic species¶
PFANT atomic lines files contains wavelength, log_gf and other tabulated information for several (element, ionization level) atomic species.
The following code calculates isolated atomic spectra for a list of arbitrarily chosen atomic species (Figure 4).
"""Runs synthesis for specified atomic species separately. No molecules or hydrogen lines."""
import pyfant
import f311
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import a99
# ["<element name><ionization level>", ...] for which to draw panels
MY_SPECIES = ["Fe1", "Fe2", "Ca1", "Ca2", "Na1", "Si1"]
if __name__ == "__main__":
pyfant.copy_star(starname="sun-grevesse-1996")
pyfant.link_to_data()
# Loads full atomic lines file
fatoms = pyfant.FileAtoms()
fatoms.load()
runnables = []
for elem_ioni in MY_SPECIES:
atom = fatoms.find_atom(elem_ioni)
# Creates atomic lines file object containing only one atom
fatoms2 = pyfant.FileAtoms()
fatoms2.atoms = [atom]
ecombo = pyfant.Combo()
# Overrides file "atoms.dat" with in-memory object
ecombo.conf.file_atoms = fatoms2
ecombo.conf.flag_output_to_dir = True
oo = ecombo.conf.opt
# Assigns synthesis range to match atomic lines range
oo.llzero, oo.llfin = fatoms2.llzero, fatoms2.llfin
# Turns off hydrogen lines
oo.no_h = True
# Turns off molecular lines
oo.no_molecules = True
runnables.append(ecombo)
pyfant.run_parallel(runnables)
# Draws figure
f = plt.figure()
a99.format_BLB()
for i, (title, ecombo) in enumerate(zip(MY_SPECIES, runnables)):
ecombo.load_result()
plt.subplot(2, 3, i+1)
f311.draw_spectra_overlapped([ecombo.result["spec"]],
setup=f311.PlotSpectrumSetup(flag_xlabel=i/3 >= 1, flag_legend=False))
plt.title(title)
K = 1.
a99.set_figure_size(plt.gcf(), 1300*K, 740*K)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("synthesis-atoms.png")
plt.show()
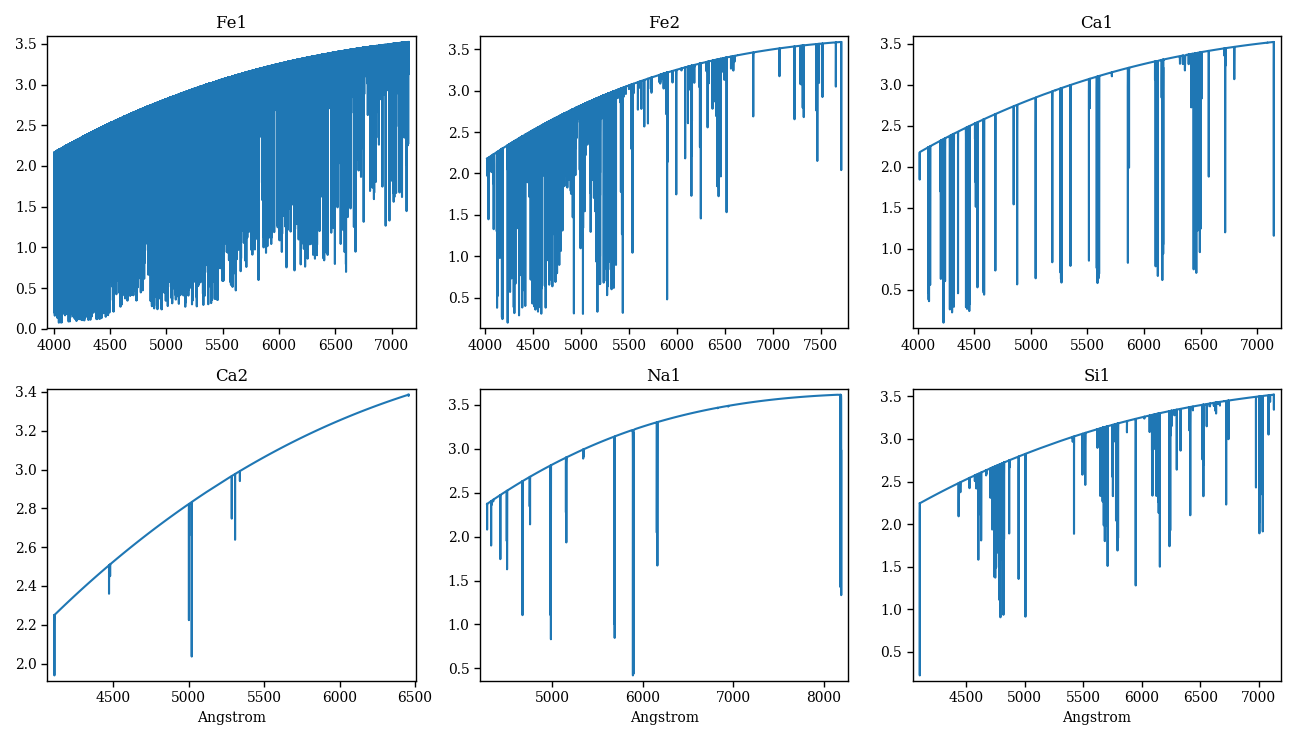
Figure 4 – atomic lines synthesized separately for each species.¶
Spectral synthesis - Separate molecules¶
The following code generates Figure 5, Figure 6, and additional plots not shown here.
"""Runs synthesis for molecular species separately. No atomic nor hydrogen lines."""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import a99
import pyfant
import f311
SUBPLOT_NUM_ROWS = 2
SUBPLOT_NUM_COLS = 2
if __name__ == "__main__":
pyfant.copy_star(starname="sun-grevesse-1996")
pyfant.link_to_data()
# Loads full molecular lines file
fmol = pyfant.FileMolecules()
fmol.load()
runnables = []
for molecule in fmol:
fmol2 = pyfant.FileMolecules()
fmol2.molecules = [molecule]
ecombo = pyfant.Combo()
# Overrides file "molecules.dat" with in-memory object
ecombo.conf.file_molecules = fmol2
ecombo.conf.flag_output_to_dir = True
oo = ecombo.conf.opt
# Assigns synthesis range to match atomic lines range
oo.llzero, oo.llfin = fmol2.llzero, fmol2.llfin
# Turns off hydrogen lines
oo.no_h = True
# Turns off atomic lines
oo.no_atoms = True
# Adjusts the wavelength step according to the calculation interval
oo.pas = max(1, round(oo.llfin*1./20000/2.5)*2.5)
oo.aint = max(50., oo.pas)
runnables.append(ecombo)
pyfant.run_parallel(runnables)
num_panels = SUBPLOT_NUM_COLS*SUBPLOT_NUM_ROWS
num_molecules = len(runnables)
ifigure = 0
a99.format_BLB()
for i in range(num_molecules+1):
not_first = i > 0
first_panel_of_figure = (i / num_panels - int(i / num_panels)) < 0.01
is_panel = i < num_molecules
if not_first and (not is_panel or first_panel_of_figure):
plt.tight_layout()
K = 1.
a99.set_figure_size(plt.gcf(), 1500 * K, 740 * K)
plt.tight_layout()
filename_fig ="synthesis-molecules-{}.png".format(ifigure)
print("Saving figure '{}'...".format(filename_fig))
plt.savefig(filename_fig)
plt.close()
ifigure += 1
if first_panel_of_figure and is_panel:
plt.figure()
if is_panel:
ecombo = runnables[i]
ecombo.load_result()
isubplot = i % num_panels + 1
plt.subplot(SUBPLOT_NUM_ROWS, SUBPLOT_NUM_COLS, isubplot)
f311.draw_spectra_overlapped([ecombo.result["spec"]],
setup=f311.PlotSpectrumSetup(flag_xlabel=i/3 >= 1, flag_legend=False))
_title = fmol[i].description
if "]" in _title:
title = _title[:_title.index("]")+1]
else:
title = _title[:20]
plt.title(title)
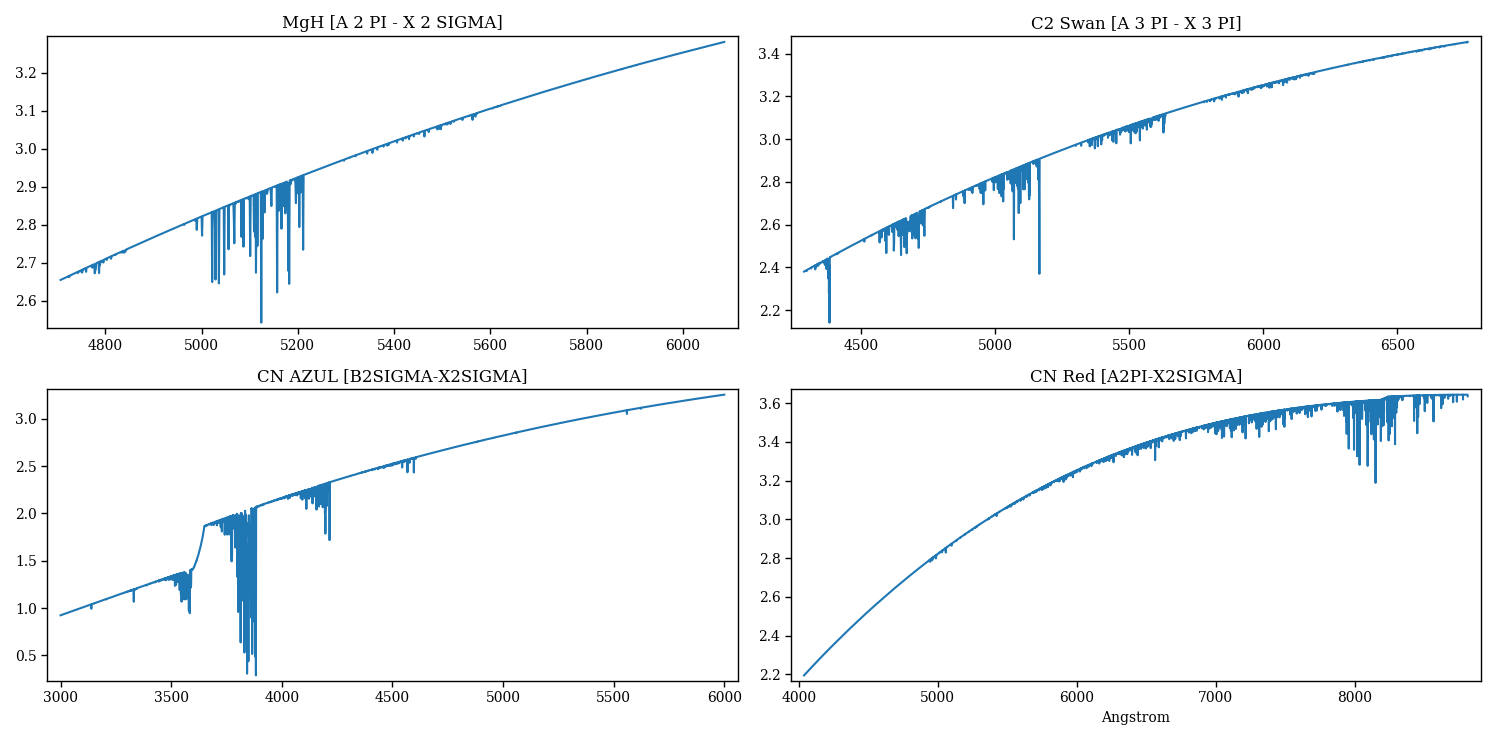
Figure 5 – molecular lines synthesized separately for each species¶
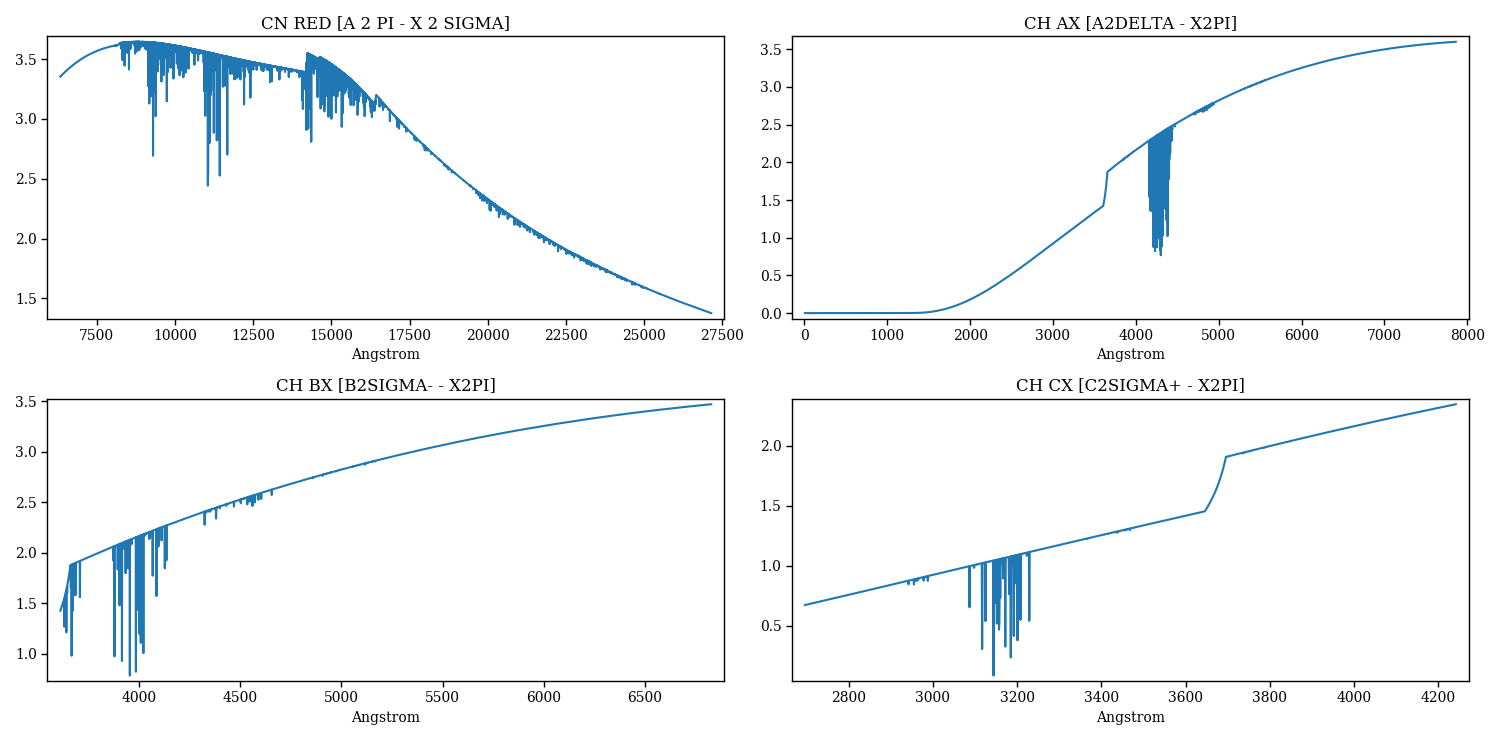
Figure 6 – molecular lines synthesized separately for each species.¶
Gaussian profiles as nulbad outputs¶
nulbad is one of the Fortran executables of the PFANT package. It is the one that convolves
the synthetic spectrum calculated by pfant with a Gaussian profile specified by a “fwhm”
parameter (Figure 7).
"""
Nulbad's "impulse response"
Saves "impulse" spectrum (just a spike at lambda=5000 angstrom) as "flux.norm",
then runs `nulbad` repeatedly to get a range of Gaussian profiles.
"""
import pyfant
import f311
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import a99
import numpy as np
# FWHM (full width at half of maximum) of Gaussian profiles in angstrom
FWHMS = [0.03, 0.06, 0.09, 0.12, 0.15, 0.20, 0.25, 0.3]
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Copies files main.dat and abonds.dat to local directory (for given star)
pyfant.copy_star(starname="sun-grevesse-1996")
# Creates symbolic links to all non-star-specific files
pyfant.link_to_data()
# # 1) Creates "impulse" spectrum
fsp = pyfant.FileSpectrumPfant()
sp = f311.Spectrum()
N = 2001
sp.x = (np.arange(0, N, dtype=float)-(N-1)/2)*0.001+5000
sp.y = np.zeros((N,), dtype=float)
sp.y[int((N-1)/2)] = 1.
fsp.spectrum = sp
fsp.save_as("flux.norm")
# # 2) Convolutions
spectra = []
for fwhm in FWHMS:
enulbad = pyfant.Nulbad()
enulbad.conf.opt.fwhm = fwhm
enulbad.run()
enulbad.load_result()
enulbad.clean()
# Appends convolved spectrum for comparison
spectra.append(enulbad.result["convolved"])
# # 3) Plots
f = plt.figure()
f311.draw_spectra_overlapped(spectra)
K = 0.7
a99.set_figure_size(plt.gcf(), 1300*K, 500*K)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("gaussian-profiles.png")
plt.show()
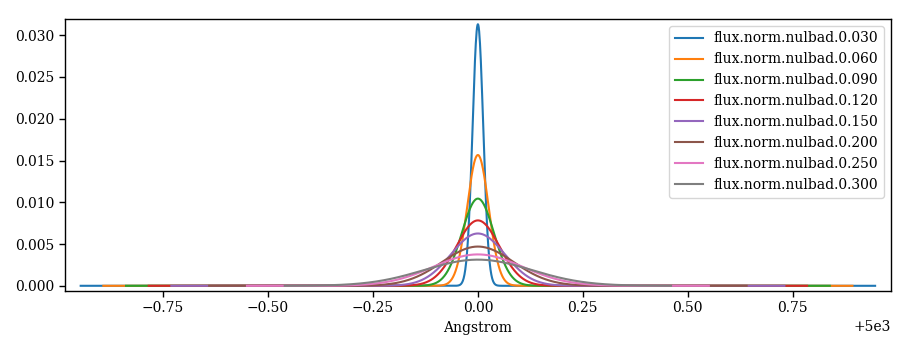
Figure 7 – Gaussian profiles illustrated for different FWHMs.¶
Plot hydrogen profiles¶
The following code generates Figure 8.
"""
Calculates hydrogen lines profiles, then plots them in several 3D subplots
"""
import pyfant
import a99
import os
import shutil
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D # yes, required (see below)
def mylog(*args):
print("^^ {}".format(", ".join(args)))
def main(flag_cleanup=True):
tmpdir = a99.new_filename("hydrogen-profiles")
# Saves current directory
pwd = os.getcwd()
mylog("Creating directory '{}'...".format(tmpdir))
os.mkdir(tmpdir)
try:
pyfant.link_to_data()
_main()
finally:
# Restores current directory
os.chdir(pwd)
# Removes temporary directory
if flag_cleanup:
mylog("Removing directory '{}'...".format(tmpdir))
shutil.rmtree(tmpdir)
else:
mylog("Not cleaning up.")
def _main():
fm = pyfant.FileMain()
fm.init_default()
fm.llzero, fm.llfin = 1000., 200000. # spectral synthesis range in Angstrom
ei = pyfant.Innewmarcs()
ei.conf.file_main = fm
ei.run()
ei.clean()
eh = pyfant.Hydro2()
eh.conf.file_main = fm
eh.run()
eh.load_result()
eh.clean()
_plot_profiles(eh.result["profiles"])
def _plot_profiles(profiles):
fig = plt.figure()
i = 0
for filename, ftoh in profiles.items():
if ftoh is not None:
mylog("Drawing '{}'...".format(filename))
# ax = plt.subplot(2, 3, i+1)
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, i+1, projection='3d')
ax.set_title(filename)
pyfant.draw_toh(ftoh, ax)
i += 1
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("hydrogen-profiles.png")
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(flag_cleanup=True)
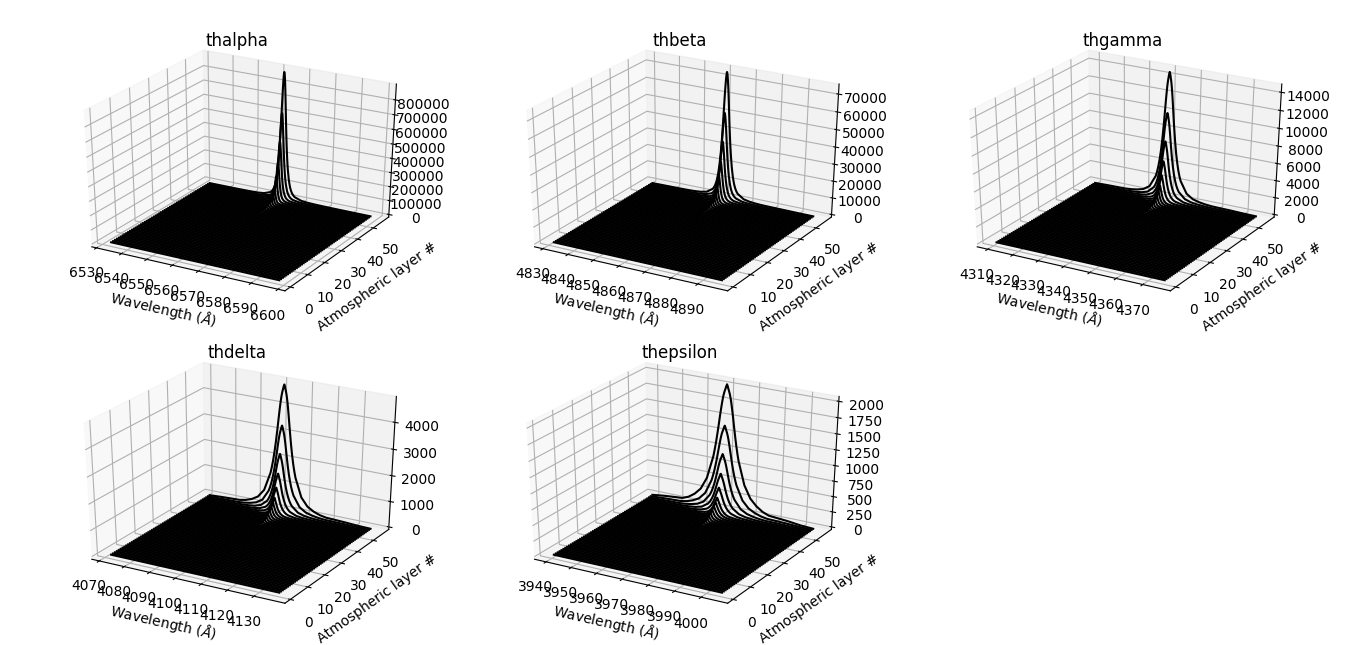
Figure 8 – hydrogen lines profiles as calculated by hydro2.¶
Import Kurucz’ molecular linelist file¶
"""
This example loads file "c2dabrookek.asc" and prints a memory representation of its first line.
This file can be obtained at http://kurucz.harvard.edu/molecules/c2/. First lines of file:
```
287.7558-14.533 23.0 2354.082 24.0 -37095.578 6063a00e1 3d10e3 12 677 34741.495
287.7564-14.955 22.0 2282.704 23.0 -37024.124 6063a00f1 3d10f3 12 677 34741.419
287.7582-14.490 21.0 2214.696 22.0 -36955.900 6063a00e1 3d10e3 12 677 34741.205
287.7613-15.004 24.0 2428.453 25.0 -37169.280 6063a00f1 3d10f3 12 677 34740.828
287.7650-14.899 20.0 2149.765 21.0 -36890.147 6063a00f1 3d10f3 12 677 34740.382
```
"""
import f311
f = f311.load_any_file("c2dabrookek.asc")
print(repr(f[0]).replace(", ", ",\n "))
This code should print the following:
KuruczMolLine(lambda_=2877.558,
loggf=-14.533,
J2l=23.0,
E2l=2354.082,
Jl=24.0,
El=37095.578,
atomn0=6,
atomn1=6,
state2l='a',
v2l=0,
lambda_doubling2l='e',
spin2l=1,
statel='d',
vl=10,
lambda_doublingl='e',
spinl=3,
iso=12)